本文介绍生存模型,属于CS2第六章的内容,也是学习CM1的寿险精算部分的先修内容。
本文不仅适用于英国精算师的考试,Jackie 在写这篇推文时也参考了北美体系的内容,所以考SOA的同学也不妨看一下。
Notation
cdf of
sf of
pdf of
Relationship between
Events that are equivalent (important relationship between
cdf of
sf of
pdf of
Chaining Survival
Conditions on
Assumptions on
The force of mortality
Typical
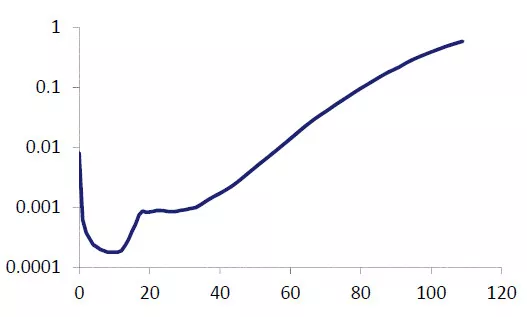
- High infant mortality
- An ‘accident hump’ at ages around 20
- The nearly exponential increase at older ages
Some Common Mortality Models
- Exponential Model: Constant force of mortality
- De Moivre Model:
- Compertz Model
- Generalized (or Modified) De Moivre Model
Actuarial Notation
Survival:
Mortality:
Deferred Mortality:
It's convention that
3 ways to calculate
Relationship between F and f
Approximate
For small
Distributional Quantities of
Mean of
Complete expectation of life:
Median of
This is the value





正在检查 Disqus 能否访问...